If terms like XML sitemaps, largest contentful paint, and anchor text optimization sound like a foreign language to you, don’t worry, you’re not alone. Search engine optimization (SEO) can be terribly complicated, but for people who just want to find a simple way to boost their organic traffic, the best free SEO tools can make this task a lot more manageable.
However, most SEO tools won’t do the work for you; they give you insight into the data and then leave you to do what you will with it. For example, keyword tools will tell you basic keyword metrics like volume and keyword difficulty, but they won’t tell you which keyword you should optimize your page for; that’s up to you to decide.
With so much of SEO relying on your experience and best judgment, there’s no better way to learn SEO than by doing it for yourself. Following this guide, you’ll learn how to use the best free SEO tools to perform foundational tasks like keyword research, on-page optimization, and backlink building. You won’t be an expert overnight, but becoming familiar with these tools and what you can accomplish with them will help you rank for profitable keywords, boost your site’s organic traffic, and introduce you to what you can achieve on your website with a knowledge of SEO.
1. Research Keyword Ideas with SpyFu
Keyword research is the most basic SEO task you’ll need to do because keywords are the heart of how search engines work. When someone performs a search, Google matches their search intent with a keyword and pulls up relevant pages that rank for it. When planning your content, you’ll need to decide which keywords you want your page to rank for so that it’s being seen by the people you want to attract to your website.
SpyFu’s Keyword Research Tool will help you find and prioritize the best keywords for your website to target. It shows you how many searchers search for a keyword each month (volume) and how hard it’ll be to rank for it (keyword difficulty). Although SpyFu is a paid tool, it does allow for free use as long as you'd like, only limiting the number of keyword ideas you’ll see in each search.
Start by heading over to the Related Keywords Tool. If you have an existing page or a specific idea of what you want to create, type in what you think people would search for to find it. For example, if you’re a design company creating a page on logo design, you might search for “examples of logo design.” If you’re not sure yet what your page will be about, keep your search broad, like “logos” or “design.”
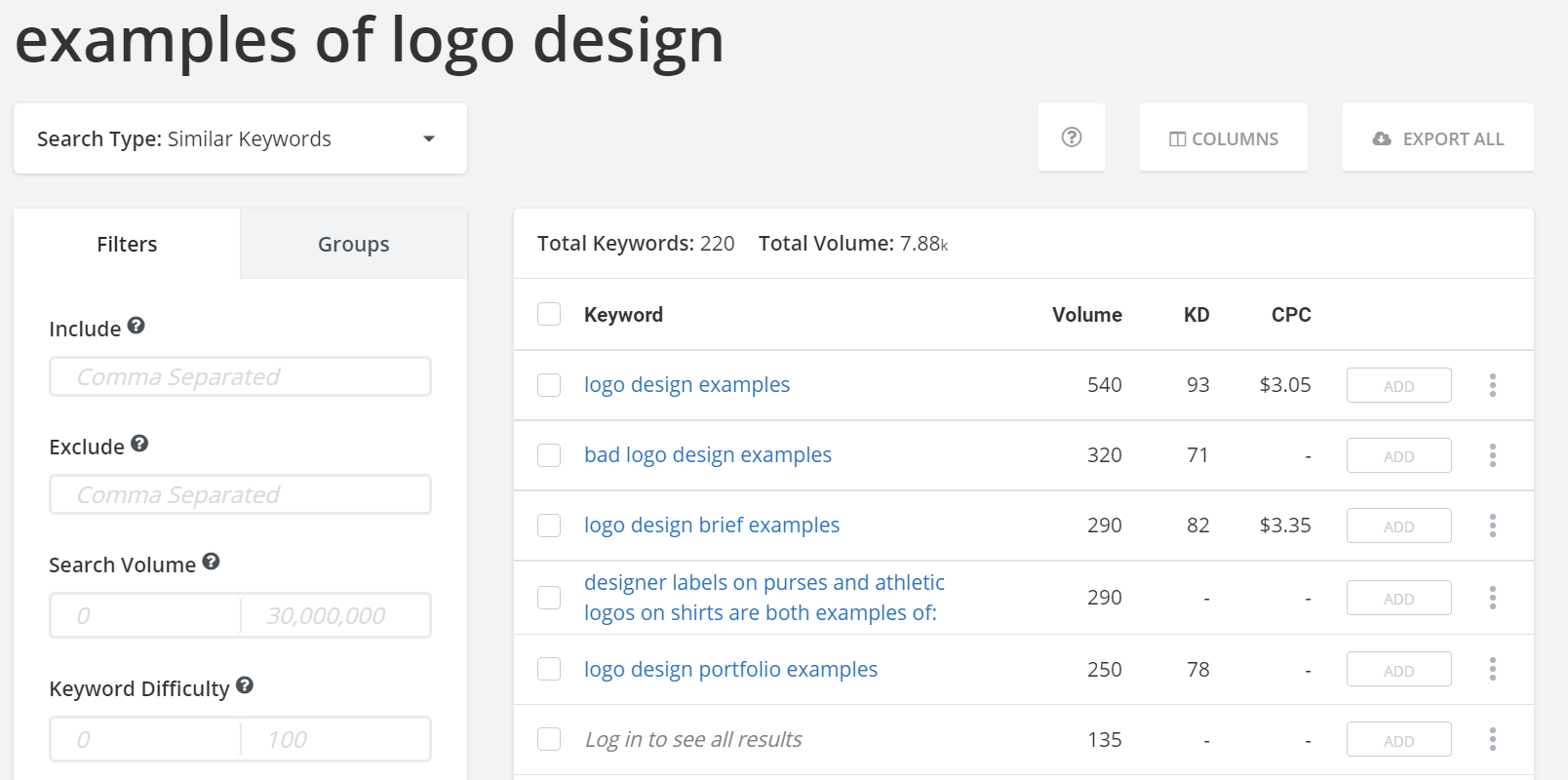
The Related Keywords Tool will give you keywords that it thinks are related to the keyword you searched for. When evaluating these different keywords, look at the volume and keyword difficulty (KD) metrics. Ideally, you’ll want to find keywords that have a high volume and low difficulty. That way, you’ve got the highest chances of ranking for a keyword that’ll get your content in front of the maximum number of people.
However, when researching keywords, be careful of falling into the metrics trap. High volumes are only valuable for you if they bring relevant searchers. For example, “instagram logo” has a search volume of 168,000 a month, but it’s unlikely to contain a lot of people interested in your design company. On the other hand, a high KD will be hard to rank for, especially for newer or smaller sites, but it’s still possible with the right SEO strategy.
Instead of basing keyword decisions on metrics alone, use search intent to find the best keywords for your page. When you evaluate keywords based on search intent, you make sure that your current or future page will match what people are actually looking for when they land on that keyword’s search engine results page (SERP). It wouldn’t make sense to optimize a page for logo design examples only to have your page talk about basic design elements. You can learn more about understanding what users want with our guide to determining search intent.
With all of this in mind, for our design company example, we might choose “bad logo design examples” as our primary keyword because it has 320 monthly searchers, a lower KD than “logo design elements,” and it matches the kind of content we’d like to make on our website. Although you can optimize your page for multiple keywords, it’s usually best to choose one primary keyword that will be the central focus of your optimizations. Once you’ve found your primary keyword to optimize for, we can move on to finding an angle to make your content stand out from the crowd.
2. Find Unique Article Angles with AnswerThePublic
AnswerThePublic is a data aggregation tool that can tell you what people search for or ask about based on a given topic. By making your content thorough and unique, you’ll not only help your readers and position yourself as an expert, but you’ll also rank better on Google, helping your bottom line. Once you’ve navigated to answerthepublic.com, simply put in the keyword you’re researching. For longer keywords like “bad logo design examples,” shorten it to one to two words for better results.
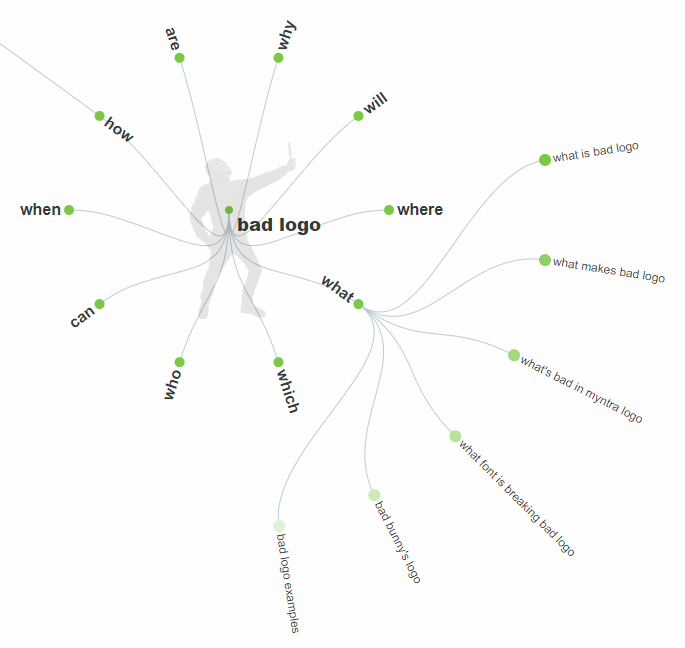
Next, scroll through the suggestions and make a note of any that might make good topics to cover in your article. For example, “what makes a bad logo” could be an interesting subsection that could complement your bad logo examples.
When you’re done looking through AnswerThePublic, you should also consider checking out some free places on the internet to better understand how you can add value to your page. We’ve collected a list of some of our favorite places, like the Google SERP, social media sites, and Quora, in our guide to finding new content ideas.
Once your research is done, get to work writing and creating. When the article draft is complete, you can move on to optimizing your post for search engines.
3. Compress Images with Optimizilla
Images are a crucial part of almost every webpage, helping your article be more engaging and educating, but when handled badly, they can slow down your page load speed, a key ranking factor for Google. A simple way to improve your image SEO is to use Optimizilla to compress your images so they take up less room and speed up your page experience.
On Optimizilla, upload your photos by clicking “upload files” and then select the files you want to compress.
Optimizilla will automatically start to compress your file, and, when done, you can download your images and add them to your article. The whole process should take no more than a couple of minutes.
If you’re having problems with finding images, consider checking out Unsplash or Canva. Unsplash has a database of royalty-free images that any site can use for free. Canva offers customizable templates to help with blog images and social media posts.
Or, try transforming your own photos though Colorcinch (formerly Cartoonize). Colorcinch is a freemium image editor and creator that is simple to use for even the least experienced designers. We like that a version of it is free for as long as you'd like and the upgrade gives you more features. Win, win! With these three sites, you should be able to quickly and easily fill your page with images that help readers engage with your content.
Image SEO doesn’t stop with compression. You should also consider:
- Adding descriptive names to your file names
- Using Alt Texts correctly
- Choosing the correct file type for the job
You can learn more about these techniques in our guide to image SEO.
4. Check On-Page SEO with Yoast
Yoast is a popular WordPress plugin that will help you audit your on-page SEO, checking your keyword density, titles, links, and more. On-page SEO refers to optimizations that happen on your website; this can include your site structure or how your individual webpages are laid out.
Yoast works at the individual page level, helping you make sure that your page is designed in a way that gives it the highest chance to rank for your given primary keyword. You can install Yoast by going to your WordPress account and, on the left-hand sidebar, clicking on “Plugins” and selecting “Add New.”
Next, type “Yoast” into the search bar, find the correct plugin and click download.
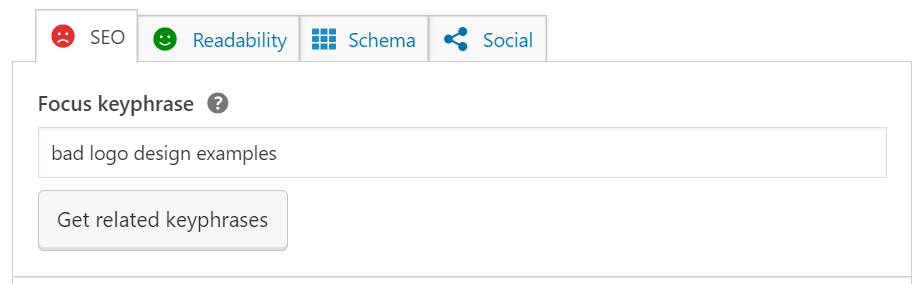
Once installed, Yoast will change your page editor, so when you scroll to the bottom of the page, you’ll see suggestions on how you can improve the SEO of your new post. Start by typing in your primary keyword in the bar that says “Focus keyphrase.”
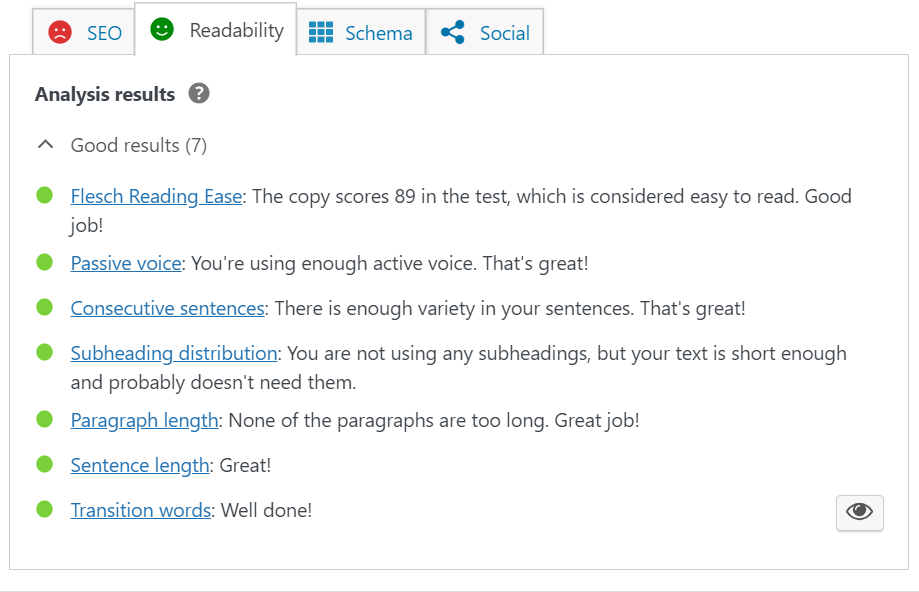
Next, scroll down or click on the tabs at the top of the page to get simple instructions on what you can do to improve. For instance, Yoast will analyze how well you’ve written your content on the “Readability” tab and give you suggestions on things like removing passive voice or adjusting your paragraph length.
Yoast, however, is not a perfect tool. Yoast itself will tell you that it has limitations and should not be taken as gospel. One thing that Yoast suggests is that your keyword should appear a certain number of times based on how long your content is— this concept is called an ideal keyword density. Ideal keyword density has been shown to be a myth, and we’d argue it can even hurt your overall SEO.
Yoast is not a silver bullet for on-page SEO, but it is one of the best free SEO tools for helping you out, especially when you’re new. It shouldn’t replace common sense, though. Remember that, for SEO, the most important factor is always user experience, so if Yoast suggests something that’ll make your article more difficult to read or grammatically incorrect, then ignore that suggestion.
Unfortunately, Yoast is only available to WordPress users. If you’re using a different content management system (CMS), consider following our on-page SEO checklist so you can optimize based on your own experience and not an algorithm.
5. Improve Existing Content with RivalFlow AI
RivalFlow compares your existing page against your competitor on the SERP that outranks you. It analyzes the two pages and shows you objectively what they answered better for a reader. And, because analysis is one thing and actual work is another, it gives you original copy to fill the gaps in your article.
One thing I love about RivalFlow is that it takes no technical skill or help from your dev team to follow through. If you can update the copy on your web page or blog article, you can use RivalFlow. And that goes a long way for writers and marketing team members who are often the ones tasked with content improvement.
RivalFlow offers premium features that allow for more customization and more pages analyzed. You can still analyze pages for free with limited options. Premium plans also start with a 14-day free trial.
6. Find Backlink Opportunities with Seobility
Backlinks are the links that connect one website to another. They are an important ranking factor for Google as they tell Google that your site is trustworthy enough for another site to link out to. Seobility is a free backlink tool that can help you start to build backlinks by finding opportunities where other websites might want to link back to your content.
The best way to use Seobility is to find your competitor’s backlinks. When you know who links back to your competitors, you can find websites that might be more inclined to link back to your own site.
To start, head to Seobility, and type in either the domain of one of your competitors or a specific page that you’re competing against in the SERP.
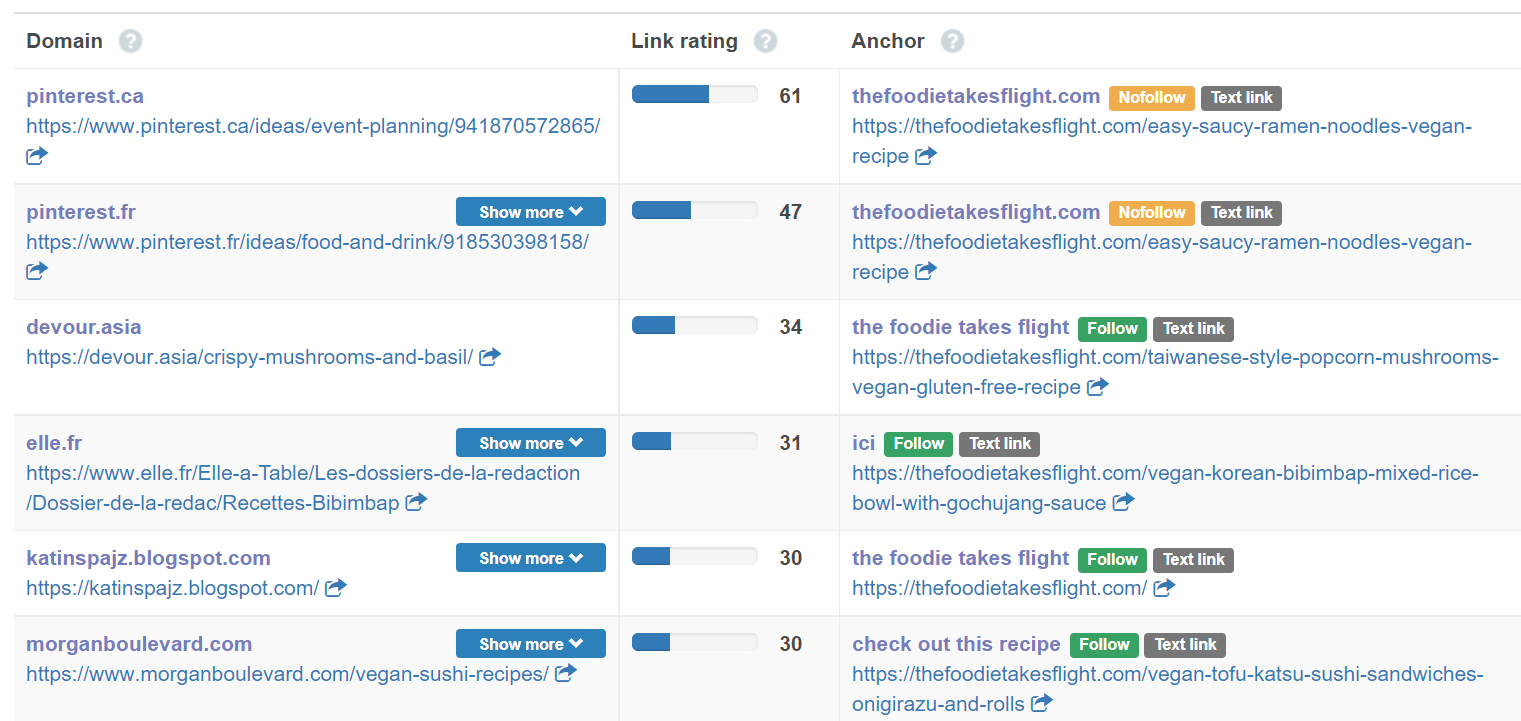
On the left, you’ll see the page that is linking to your competitor. The center column tells you how “strong” the link is as far as giving positive signals to Google. The right column shows you what page of yours they’re linking to and what anchor text they’ve used.
Search through these links and find pages that might link to you. Look for directories that include a number of pages on one topic and ask to have yours included or, if your content is better than your competitor’s, email the webmaster and ask for your page to replace your competitor’s.
Backlinking is one of the hardest jobs that an SEO does, and even the most seasoned veterans should expect far more failures and non-responses than backlink wins. To learn more about how to improve your odds, check out our guide to finding easy backlink opportunities.
7. Troubleshoot with Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is the main way to understand how your website performs on Google Search. GSC is a free SEO tool from Google that makes it easy to know whether your page is searchable on Google and troubleshoot any page experience issues that could hurt its rankings.
Although GSC is free, you’ll need to have a Google account to begin your website’s GSC setup process. If you’re completely new to GSC, follow these instructions from Google to set up, verify, and learn how to use the basic functions of Search Console.
The most basic use of GSC is to make sure your new page has been indexed and is searchable on Google Search. To do this, sign in to your GSC account, and then type your page’s URL into the search bar along the top of the page.

When you search that URL, Google will tell you whether it’s indexed (searchable on a SERP) and when it was last checked by Google.
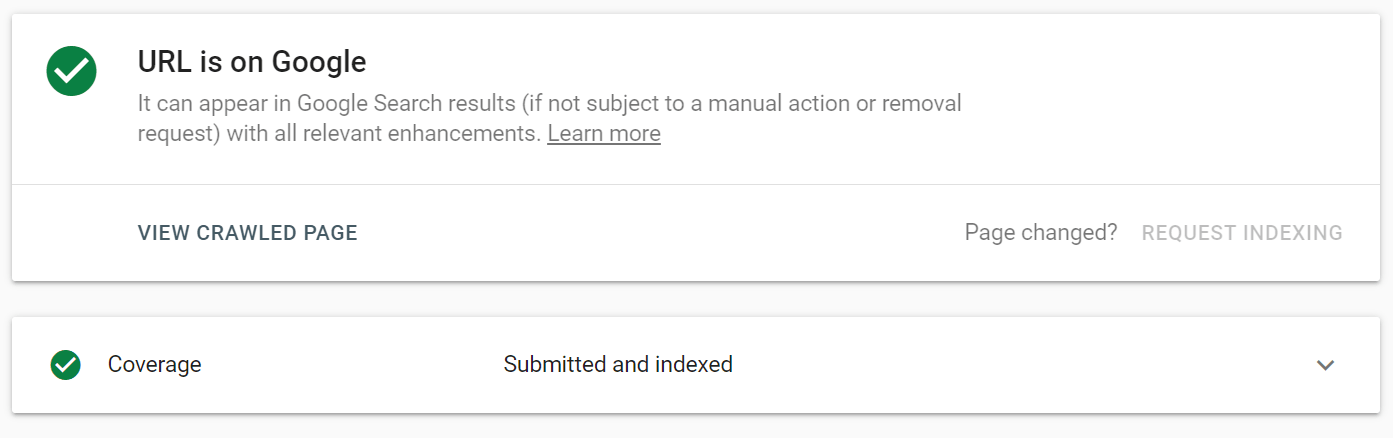
If your page isn’t indexed or if you’ve changed it a lot since it was last crawled, you can click on the “Request Indexing” button to have Google take a look ASAP. This way, webmasters like you can keep Google up-to-date on your website, making sure the newest version of your website is on Google, ready to be found by searchers.
The other way to use GSC is to check for any user experience errors. Go back to the GSC homepage and click on “Page Experience” on the left sidebar. On this page, Google will tell you about any issues found with your website, from problems that affect user experience to security issues.
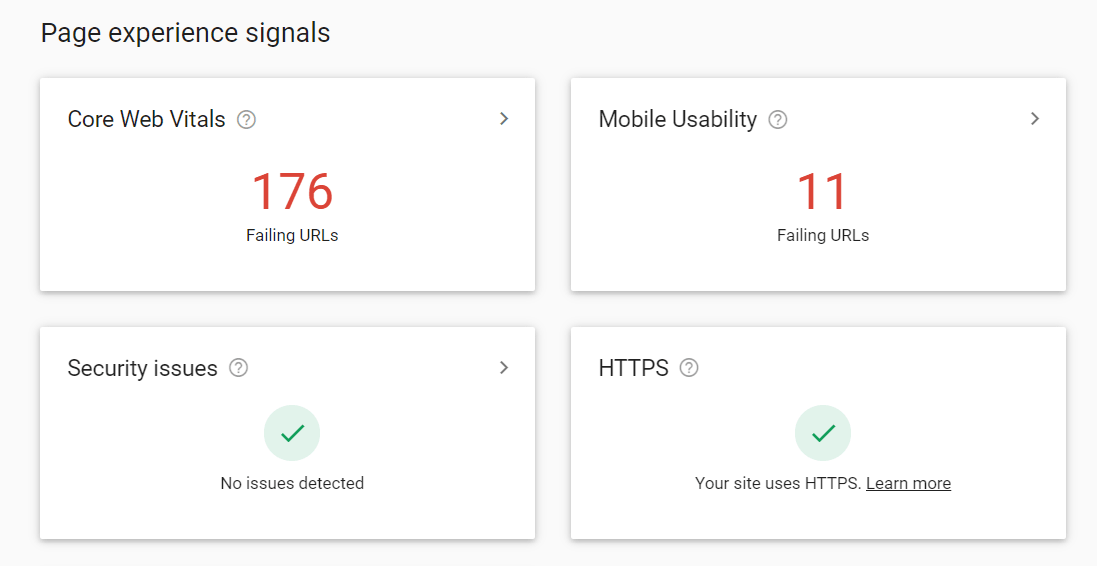
To start fixing these issues, click on one of the three clickable squares on the page, for example, “Core Web Vitals.” From here, you’ll see a list of issues pertaining to Core Web Vitals on your website; click on one to get more details.
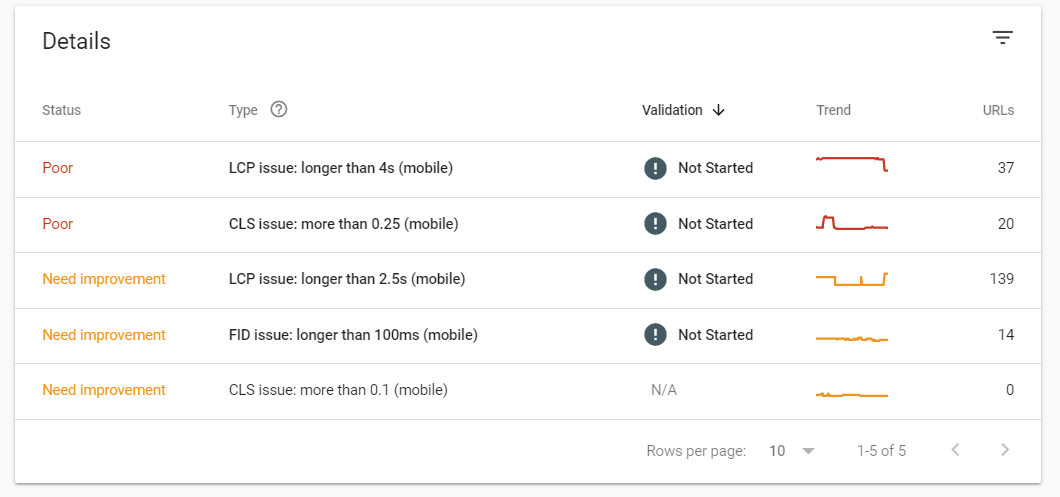
The next page you’ll be taken to will tell you which pages on your website have this problem. You can learn about how to fix the problem by clicking on the “Learn More” button.
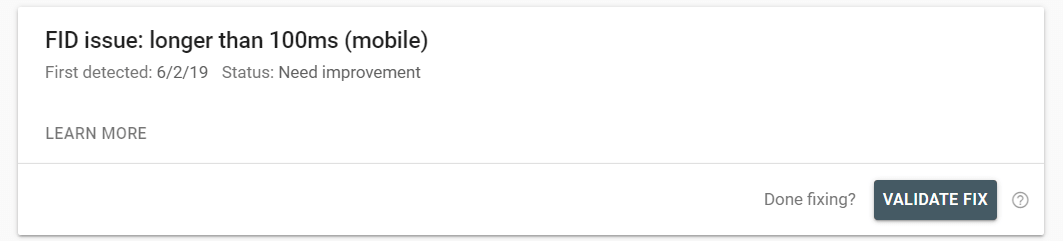
In some cases, fixing the problem might be beyond your abilities. Although you should aim for no problems, the reality is that some fixes will be out of reach. Try to fix what you can and accept what you can’t until you can devote more resources to it.
If you fix the problem, click the “Validate Fix” button to have Google recheck these URLs and validate that your website is no longer having this issue.
This is just a taste of what you can do with GSC once you’re more experienced with all of its tools. Read our guide to finding insights on Search Console to learn more.
8. Track Your Progress with Google Analytics
Google Analytics (GA) is the best free SEO tool for tracking your website so you can understand if your new SEO optimizations are hurting or helping your content efforts. For people new to SEO, GA is the most useful and hardest to learn tool on our list. GA is a dense jungle of so much data that it can be hard to know where to look for the insights you need. However, once you know where to look, you shouldn’t have problems finding basic data that can help you track your website’s performance.
Before you begin, you’ll need to have your GA set up and connected to your website so that it can collect data for you. Follow these instructions to get your GA account off the ground. The sooner you do this, the better, as GA will need at least a couple of months to collect enough data to be helpful to you.
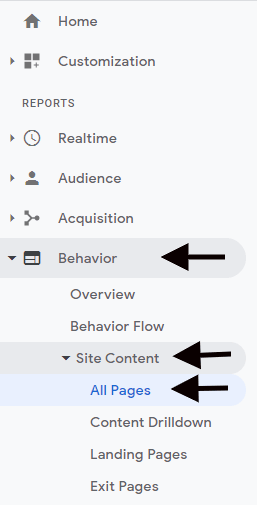
Once that’s all done, you can use GA to find out how your SEO efforts affect the number of organic visitors landing on each of your individual webpages. Start by going to the left-side menu and then clicking on “Behavior,” “Site Content,” and then “All Pages.”
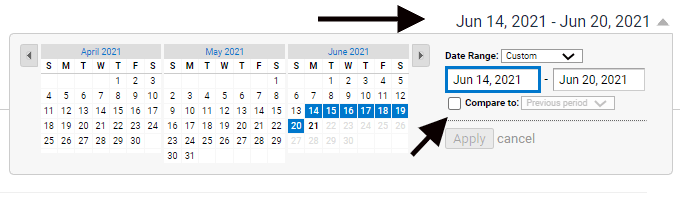
On the view that pops up, adjust the time range, so you know what data you’re looking at. Click on the date in the top-right corner and adjust the numbers. You should also set a comparison time frame so you can see how things have changed. To do this, click on the “Compare to” box. Ideally, you’ll want to compare two larger sample sizes to get the best results, like the last two months compared to the previous two months. If you’re looking at smaller sample sizes, like a three-day comparison, start the comparison dates on the same weekday, as traffic can change a lot based on the time of the week you’re looking at.
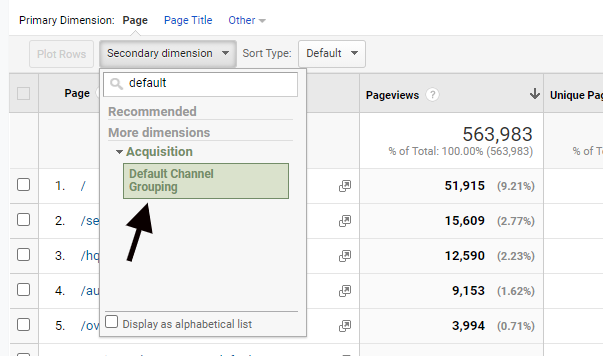
Now you need to narrow results to solely organic views. Click on “Secondary dimension” and choose the “Default Channel Grouping” option.
Then, click on “Advanced” and add a filter for “Default Channel Grouping” containing “Organic.”
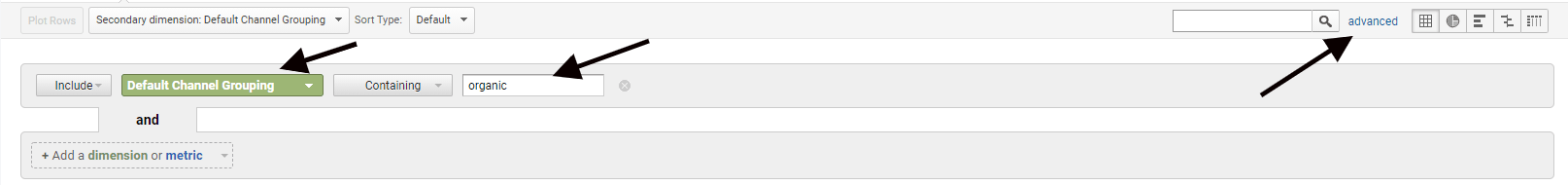
At this point, you should be left with a list of the organic results compared across two time frames for each page on your website. If you only want to find a single page, go back to the advanced section, click on “Add a dimension or metric,” select “page,” and then add the URL slug of the page you want to see. For example, for https://www.spyfu.com/blog/the-types-of-backlinks/, you would only include /blog/the-types-of-backlinks/.
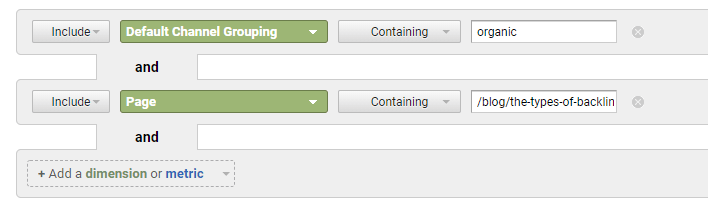
After all of that, you’ll be left with the organic search data of a page or pages over a given period of time. As you become more familiar with GA, getting to this view will get a lot faster.
With this information, you can better understand how your pages are doing. If traffic is going up or going down, you can try to figure out why and what you can do to replicate it or fix it. If your page has been doing well for over a year and it’s started to experience a downturn in traffic, it might just need a refresh. Content refreshes help old content stay relevant and reclaim its traffic numbers, and over time every page will need a refresh if you want them to continue to perform.
This is just a single example of how you can use GA to understand your website’s performance. If you want to learn more, take a look at our guide to GA for beginners, where you can find out how to set goals, set up views, and much more. As well, you might consider getting your Analytics Certification, a free course from Google that’ll help you get the most out of GA.
Take Your Next Step into SEO with a Free Certification
Tools can only take you so far and can never truly replace experience and knowledge. Once you get familiar with these free SEO tools, you’ll want to expand your understanding of SEO so you can start optimizing your site and pages even more. Take a look at this list of free SEO certifications to see how you can improve your SEO skills and branch out into more complicated and impactful SEO strategies to help your website maximize its organic traffic potential.

