In this guide, we are going to clearly explain the difference between on-page versus off-page SEO, their importance, and the key factors that impact each one. While these are certainly separate practices, you should always think about it as on-page AND off-page SEO. A great SEO strategy considers both elements equally.
In today’s competitive SEO market, having amazing content is only the start. Ranking well in the SERP takes more than finding the right keywords and writing an article. You need to consider the structure of your website and the technology used to create it and how that impacts both readers and search engine crawlers.
Further, it includes getting high-quality backlinks and get your readers to share your site with their networks. All of this contributes to the overall strength of your domain.
Understanding what goes into nailing both on-page and off-page SEO will level up you content while increasing it’s ranking potential.
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to optimizing the content, HTML source code, and other technical aspects of your website to improve its relevance and visibility to search engines. That includes everything from the technology you rely on to build the website to the way you use the words on the page. These are things you have complete control over and are the single most powerful tools you have for impacting rankings in the SERP.
When you nail on-page SEO, it helps search engines understand what your website is about and how relevant it is to specific search queries. By optimizing these on-page elements, you can increase the chances of your website ranking higher in the SERPs for targeted keywords and phrases.
Key On-Page SEO Factors
Here are some of the most important practices and technical options to consider for on-page SEO:
Content Optimization
Search engines prioritize websites that provide high-quality, relevant, and engaging content that aligns with user intent. To optimize your content, you should:
- Conduct thorough keyword research to identify relevant topics and phrases
- Create comprehensive, well-structured, and easy-to-read content
- Optimize your content for target keywords without over-stuffing
- Include relevant images, videos, and other multimedia elements
- Ensure your content is unique and provides value to your readers
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
Content structure is one of the first things people think of when they hear the phrase “on-page SEO.” A well-structured page helps search-engine crawlers parse the information you’re writing about and makes it easier for readers to understand.
Header tags are HTML elements that help structure your content and provide a hierarchical outline. Search engines use these tags to understand the context and importance of different sections within your content. To optimize header tags, you should:
- Use header tags appropriately and in a logical order
- Include relevant keywords in your header tags
- Avoid keyword stuffing or using header tags solely for styling purposes
As you’re writing a new landing page or blog post, it’s important to use headings to differentiate distinct sections.
- H1 tags are used for the title of your page.
- H2 tags are used for the primary subheads on the page.
- H3 tags are nested within H2 tags to break up the text further.
Here’s a framework of what it might look like:

Whenever readers or crawler bots land on your website, this structure will help them get a sense of what they’ll learn by reading deeper. Because crawlers assign top priority to your H1 tags, followed up H2, then H3, etc., it’s important to include your target keyword in the H1 and relevant H2 headings. That will help the article rank higher by signaling relevancy to the search query that keyword targets.
Using headings is the best way to provide a snapshot of how valuable your website is to people searching for a specific keyword. It breaks up the text, increasing readability, and it provides much-needed structure to what would otherwise be a long blog of text. The experience of reading your content is just as important as the information you include. You can be as relevant as you want, but if no one can read it, you won’t be able to rank well.
Title Tags
Title tags are the HTML elements of your site that tell search engines what title to display in the SERP. Located in the <head> section of your website, tags make sure that the title you created is always correct, regardless of how readers interact with it.

Here are just a few places that will pull the title tag:
- Entries in the SERP
- Browser tabs
- Social media posts
When you define the title of your page, make sure it is unique to that individual page and includes the keyword you’re targeting. Doing so will ensure that every page on your website is different from the others, making it easy for web crawlers to get a picture of everything your content has to offer.
Setting the correct title tags also guarantees that anytime your content is shared, it uses the correct title. Social sharing is an important aspect of off-page SEO, and an incorrect title can hurt your ranking potential.
Meta Descriptions
Your meta description is one of the first things a searcher sees when they encounter your website in the SERP. They are HTML elements that provide a brief summary of your web page's content. They are displayed in the SERPs and can significantly impact click-through rates (CTRs).
Outside of the title and the URL, it’s your best chance to explain the value of your content and get people to click through. Meta descriptions also provide that information to search-engine crawlers, making it easy for them to figure out what your site is about and bring it back to be indexed.
Here’s an example from our article on how to find long-tail keywords in Google:
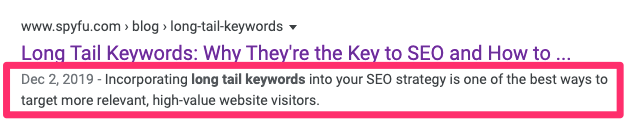
When you’re writing a meta description for any page on your site, there are a few things to keep in mind to make sure you’re getting the most on-page SEO value from it:
- Always include the keyword; it will be bolded when people encounter your site in the SERP.
- Keep meta descriptions under 160 characters; Google will truncate anything longer.
- Make sure it conveys the value your article will provide to potential readers.
By including these three elements, you’re optimizing each meta description to not only make it easy for search engines to find and index your content but also make it easy for readers to understand why they should click. Doing so will increase your potential click-throughs and provide searchers with the most valuable information up front.
URL Structure
A well-structured URL can help search engines understand the content and hierarchy of your website. When you’re first building your website, it’s important to consider how the URL structure you choose will impact all of your future pages. There are two basic ways to set up a blog, either as a subfolder or a subdomain; we suggest using a subfolder.
That’s why our blog looks like this:
https://www.spyfu.com/blogInstead of this:
https://blog.spyfu.comThe first format uses a subfolder and has some significant advantages from an SEO perspective. Not only does it make it easier to track your blog’s performance, it shares authority with your main website. As a result, high-quality backlinks to your blog help the rank of your main website and vice versa. When you’re using a subdomain, this reciprocal relationship doesn’t exist, making it harder for both sites to rank well in the SERP.
The only caveat with creating subfolders is that you need to keep the number of folders to a minimum. This creates a flat site structure that’s easier for search engines to crawl.
To optimize your URLs, you should:
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich URLs
- Keep your URLs concise and easy to read
- Avoid using unnecessary parameters or session IDs in your URLs
When you’re creating articles, you should also think about how to incorporate the target keyword for each page in the most succinct way possible. Take this blog, for example; we structure the URL as:
https://www.spyfu.com/blog/on-page-vs-off-page-seoInstead of this:
https://www.spyfu.com/blog/on-page-vs-off-page-seo-whats-the-differenceMany content management systems, such as WordPress, will automatically set your URL as the title of the post. It’s important to edit this whenever you create a new page on your site. Using shorter URLs that focus on the keyword also looks better in the SERP and to potential readers.
Whenever anyone searches for your website, they’ll also see the URL and be able to quickly parse what the page is all about.
Image Optimization
Optimizing images can improve your website's user experience and load times, which are important factors for both users and search engines. To optimize your images, you should:
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich file names for your images
- Compress your images to reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality
- Include relevant alt text for each image
Image alt text is the text that appears when images are not displayed on your website. While it’s primarily a way for you to describe the content of images when they don’t load, or when website visitors are using a screen reader, choosing the right image alt text is a vital part of on-page SEO. When a search-engine crawler reads your site, they’ll be able to parse these HTML attributes faster than the image file as well.
Writing image alt text is a pretty straightforward affair, but it’s easy to overlook or to do poorly. Here’s a picture of some manatees that we’ll write alt text for:

For the sake of example, let’s call the image file manatee.png. A good example of what your image alt text might look like:

Now, when a reader lands on your site and the image isn’t displayed, or when they’re using a screen reader to parse the page, they’ll understand what the image displays even without seeing it.
You should always try to include the keyword in your image alt text as well, but in a way that doesn’t pull focus away from the accessibility value of the alt text itself. Image alt text needs to add value for the people who rely on it.
Site Structure and Internal Linking
A clear and logical site structure can improve the user experience and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your website. Internal linking helps search engines understand the relationships between different pages on your site and can also distribute link equity (ranking power) throughout your website. To optimize your site structure and internal linking, you should:
- Create a well-organized and intuitive site structure
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text for your internal links
- Implement a flat site architecture (fewer clicks from the homepage to any given page)
When you’re creating this content, it’s important to consider how all of it fits together to provide readers with the best possible browsing experience. Not only does internal linking making it easier for bots to crawl your site quickly, but it encourages readers to go deeper into your site as well.
You’ve already experienced this on-page SEO tactic in this very post. We link to a number of different articles from our blog to offer more information on the various different topics we’ve covered so far. Take these two from the section on meta descriptions:
We link out to two different resources: one that digs into the topic of meta descriptions and one that explains how to find long-tail keywords. This gives readers the opportunity to learn more about one or both of those topics outside of its impact on on-page SEO and connects the new post with existing ones.
By connecting the post with existing content, we’re making it easier for web crawlers to find the page. Since they already have the meta description and long-tail keyword articles in the index, the next time a bot goes out to crawl the page, they’ll quickly find the new post and bring it back to the search engine.
This builds a map of the content on your site and provides valuable context for search engines to learn how authoritative and comprehensive your site actually is.
Page Speed and User Experience
Search engines prioritize websites that provide a positive user experience, including fast load times and mobile-friendliness. To optimize your page speed and user experience, you should:
- Minimize HTTP requests by compressing files and enabling browser caching
- Optimize images and other multimedia elements for faster load times
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and responsive
- Improve Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, Interaction to Next Paint, and Cumulative Layout Shift)
Site Speed and Responsiveness
Sites cannot rank high unless they are fast. It is critical that the technology you use to run your site is optimized to load quickly across multiple different browsers and mobile devices.
With over 60% of Google searches performed on mobile devices in 2019, making sure your site is mobile responsive is a big part of on-page SEO. If your site performance suffers when people use a mobile device, that will decrease your site’s ranking over time.
Google provides you with a tool to test out your site that tells you what needs to be changed to be considered mobile-friendly.
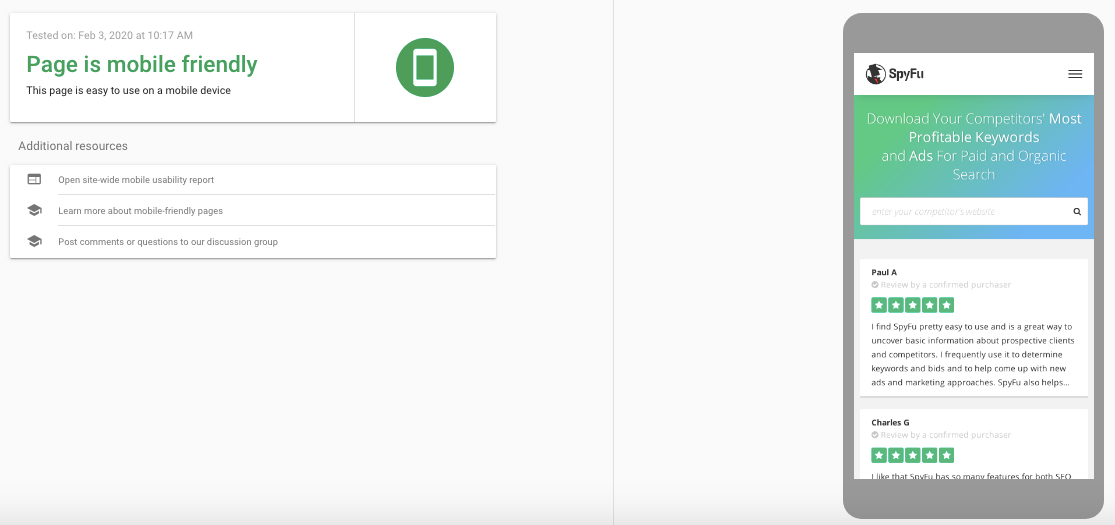
When you use the tool, it will provide you with a screenshot of how your page appears on mobile and will offer suggestions for what needs to be improved. As you’re optimizing your on-page SEO, these diagnostic tools can help you identify areas of opportunity or confirm that recent changes are making a positive impact.
By focusing on these key on-page SEO factors, you can improve your website's visibility and rankings in the SERPs, ultimately driving more organic traffic to your site.
What Is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to optimizing various ranking factors outside of your website itself to improve its visibility and authority in search engine results. This includes activities like link building, social media promotion, and local citations.
A good off-page SEO strategy will grow brand awareness, boost engagement with your content, and highlight how relevant your site is to SERP users. Many of the choices you make in your on-page SEO strategy will also affect how well your off-page SEO is overall. That’s why the guide to on-page SEO to off-page SEO is less about the differences and more about how to use both together.
Key Off-Page SEO Factors
Here are some of the most important off-page SEO factors to consider:
Link Building
Link building is the process of acquiring high-quality backlinks from other reputable websites. Backlinks are essentially votes of confidence from other websites, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy.
To build high-quality backlinks, you should:
- Create valuable and shareable content that naturally attracts links
- Engage in outreach and guest blogging opportunities
- Leverage broken link building and resource page link building tactics
- Monitor and disavow any low-quality or spammy backlinks
One of the primary drivers of a successful off-page SEO strategy is your backlink profile—the quality and quantity of outside websites that link to your page. Gaining relevant links from authoritative websites helps boost your ranking ability considerably.
The reason for this boost is due to how search engines classify relevant content. Basically, when other resources link to your website, they transfer some of their link equity to your content, making it more valuable both to search engines and to readers. There are a few factors that go into a high-quality backlink:
- Anchor text used
- Domain strength of the site
- Relevancy to the content of your post
When these come together, it tells search engines that you are creating relevant and optimized content on your website and others think so as well. With SpyFu’s Backlink tool, you can discover high-quality backlinks for specific keywords, see what URLs are linking to your content, and what URLs are linking to your competitors.
Here’s an example of backlinks for content that ranks for the keyword seo tools.
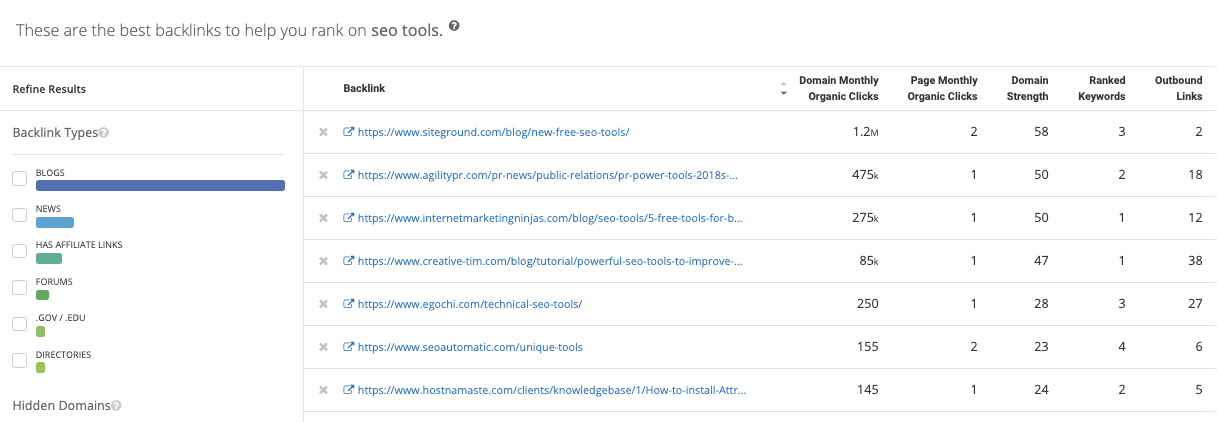
When you’re thinking about creating content for a specific keyword, this data helps you understand the type of backlink profile required to rank well in the SERP. It also gives you an idea of why and how certain URLs link to content for that keyword, which you can use to inform the structure and content of your own article.
When entering a competitor’s website, this information helps you find other areas of opportunity and see what different kinds of blogs favor your competition.
This can be an ice breaker in forming relationships with other websites in your industry. That way, you can reach out and see if they’re interested in linking to new content that you believe will be relevant to their audience.
Domain Strength
Domain strength is a measure of how authoritative your site is, according to search engines. Also referred to as domain authority, it often assigns websites a score on a scale to 100. Truly, though, we see high-authority sites rating in the high 70s and 80s, so be mindful of that as you run your research.
Here are some of the factors that affect domain strength:
- Your link profile
- Overall website traffic numbers
- Relevancy to the search query
- Visitor experience
Everything we’re talking about today can impact your score, both in the on-page and in the off-page SEO sections. Think about domain strength under the umbrella of relevancy.
The more relevant your content is, the higher your domain strength can be.
When you nail that core idea, everything else will fall in place. Relevant content includes the right keywords and semantic variations. It pulls in traffic and links because the content is relevant, and visitors can easily learn from the information.
Social Media Promotion
Social media can be a powerful tool for promoting your content and increasing its visibility. By actively engaging with your audience and sharing your content on social media platforms, you can attract more traffic, backlinks, and social signals (shares, likes, comments), which can indirectly impact your search engine rankings. To leverage social media for off-page SEO, you should:
- Create and maintain active social media profiles on relevant platforms
- Share your content and engage with your audience regularly
- Collaborate with influencers and industry leaders to amplify your reach
While the connection between social sharing and ranking potential can be hazy, content that’s shared will frequently rank higher in the SERP. The likely reason for this is due to relevance and timeliness.
The best way to make an impact on this off-page SEO component is by adding a social sharing option to your content. We do this for each of our blog posts:
It’s a subtle reminder that if the reader finds our content valuable, they can easily share it with the click of a button. This increases the potential for every article we create to be shared and can make a positive impact on our ranks as a result.
But social media isn’t the only place to share content; finding interesting ways to distribute your content to relevant audiences can positively impact your ranking as well.
Every public share of your website can impact how well your content ranks in the SERP. A great off-page SEO strategy will include relevant forums, websites, and communities to share your content in.
Here are just a few:
Each of these platforms has an engaged audience, whose members share vast amounts of information with one another. But you have to be careful: shamelessly promoting your content in a forum won’t work. Posts like this from reddit can be a great place to share your thoughts.
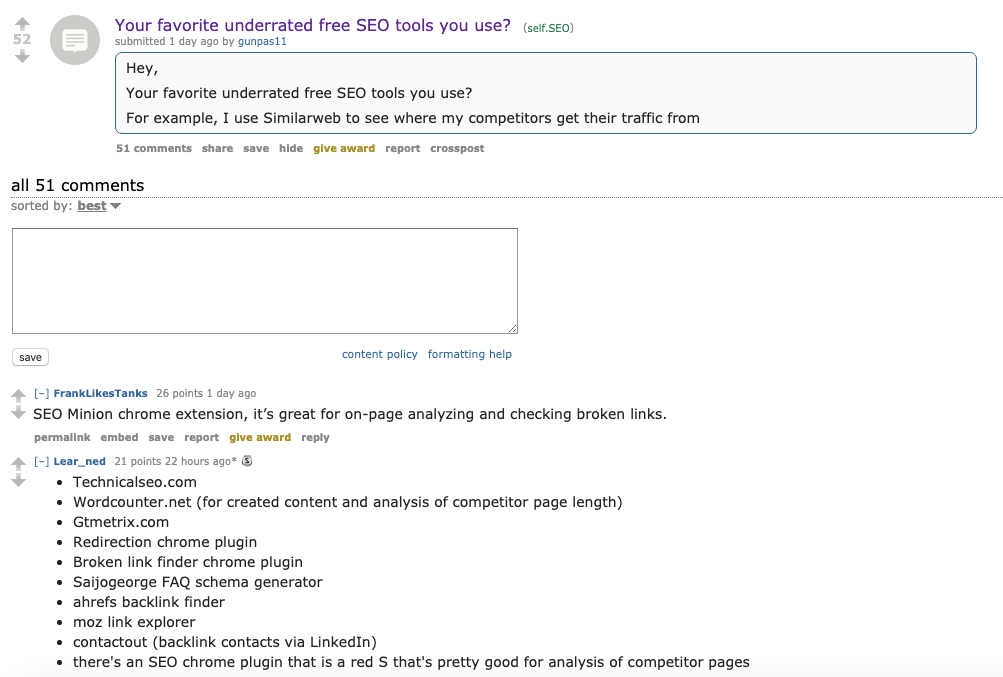
It’s important to be an active member of each community you think is relevant. Not only will that help you share your own knowledge and expertise, but it will also give you the benefit of the doubt when linking to a piece of content you create.
These communities can also be found in private Facebook or Slack groups. There are any number of different distribution networks to be found just about anywhere; you just have to know where to look.
Local Citations and Listings
If you have a local business, it's essential to optimize your online presence for local SEO. This includes claiming and optimizing your business listings on directories and review sites, as well as ensuring consistent and accurate citations (mentions of your business name, address, and phone number) across the web. By improving your local citations and listings, you can increase your visibility in local search results and attract more foot traffic to your physical location.
Local Citations and Listings
If you have a local business, it's essential to optimize your online presence for local SEO. This includes claiming and optimizing your business listings on directories and review sites, as well as ensuring consistent and accurate citations (mentions of your business name, address, and phone number) across the web. By improving your local citations and listings, you can increase your visibility in local search results and attract more foot traffic to your physical location.
Value both On-Page AND Off-Page SEO
With a strategy that combines both on-page and off-page SEO, you’re giving your website the best chance it has to rank in the SERP. With on-page SEO, you build a site that’s tailored to specific keywords; with off-page SEO, you make sure people are aware of the content you’re creating.
When you think about on-page versus off-page SEO, it’s really about how to build and distribute your content in such a way that it appeals to both search engines and website visitors. You’re crafting an experience that makes interacting with your content easier while also boosting your ranking potential.

